Case Study: Deploying Large- Scale AI Training Network Over Ethernet
ByteDance’s Challenge
AI training traffic places unique demands on the network. GPU workloads generate synchronized elephant flows that are inherently bursty. As such, network links can be saturated within microseconds, making tail latency a dominant factor, while the slowest flow determines when the next training iteration can begin.
ByteDance found that traditional Ethernet approaches struggled under these conditions. Techniques based on ECMP hashing and source-based forwarding led to uneven link utilization, congestion and unpredictable performance, especially as cluster scale increased.
ByteDance needed an Ethernet-based solution that could deliver:
- Predictable, high-performance GPU training at scale
- Improved job completion time with minimal tail latency
- Fast, disruption-free recovery from unavoidable link failures
- Operational simplicity aligned with modern network operations and automation tools
- Open Ethernet-based architecture enabling vendor diversity
ByteDance’s ultimate goal: Achieve performance characteristics expected from purpose-built AI fabrics, while retaining the flexibility and openness of Ethernet.
Why DriveNets Stood Out
As ByteDance evaluated Ethernet-based AI networking solutions, DriveNets Network Cloud-AI emerged as the best fit for hyperscale AI training.
Its scheduled fabric architecture breaks traffic (packets) into smaller, equal-sized cells that are sprayed across the fabric, ensuring 100% fabric utilization without requiring traditional ECMP hashing. To prevent congestion and collisions, especially during intensive GPU workloads, the system uses receiver-based scheduling. This means that data is sent only when the receiver is ready, delivering consistent and predictable performance regardless of traffic patterns.
In addition, the DriveNets’ scheduled fabric provides zero-impact failover. Link health is monitored in hardware, and when a failure occurs, traffic is automatically re-steered across remaining links within microseconds, without disrupting training jobs. This allows large GPU clusters to continue operating smoothly despite frequent and inevitable link failures at scale.
Solution
After testing multiple Ethernet-based solutions, ByteDance deployed DriveNets Network Cloud-AI in its production backend network. The solution is built on white box switches using Broadcom ASICs running DriveNets software.
Deployment details
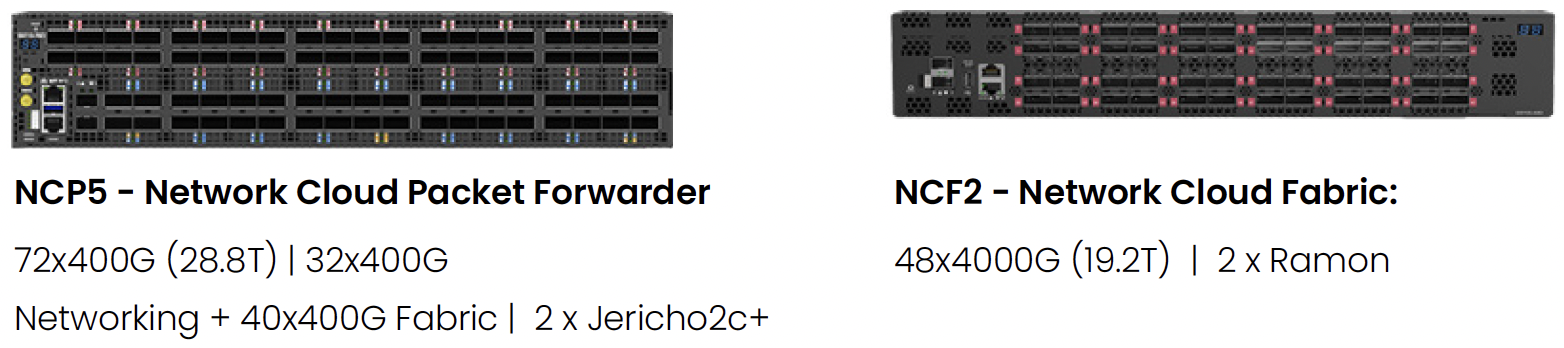
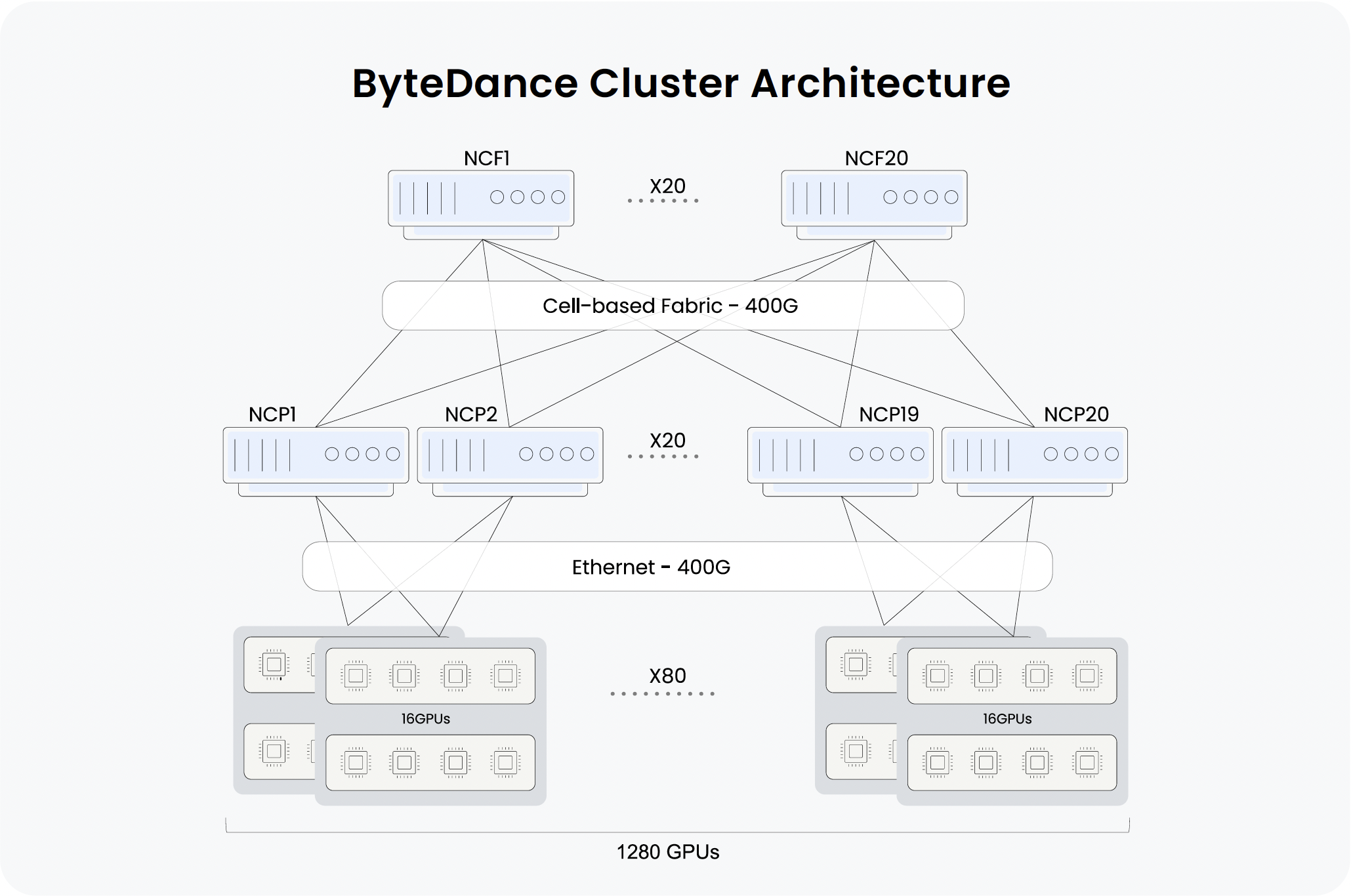
- Compute: 1280 GPUs
- Hardware: Cluster of 20 NCPs (top-of-rack switches) and 20 NCFs (fabric switches), built with UfiSpace white boxes and powered by Broadcom Jericho and Ramon chipsets
- Software: DriveNets Network Cloud software orchestrating and managing the entire cluster fabric
ByteDance deployment hardware components:
Benefits
ByteDance partnered with DriveNets and Broadcom to test a scheduled fabric over several months. Given the strong results, ByteDance deployed DriveNets Scheduled Ethernet Fabric in its production AI training environment in July 2024 with great success.
Key points following deployment:
- High performance: In internal testing, the scheduled fabric delivered up to 22% improvement for reduce-scatter workloads, up to 21% improvement for all-gather workloads, and up to 119% improvement for all-reduce workloads compared to traditional Ethernet.
- Improved job completion time: Reduced tail latency enables faster iteration and improved training efficiency.
- Operational simplicity: DriveNets’ scheduled fabric cluster offers life cycle management tools such as independent upgrades, gRPC, SNMP, and ZTP, all aligned with ByteDance’s existing network operations and automation workflows.
- Open architecture: DriveNets solution is agnostic to GPU, NIC and optics vendors, simplifying procurement and hardware availability.
- Resilient AI fabric: Hardware-based failover delivers recovery with minimal impact on training jobs.
ByteDance partnered with DriveNets and Broadcom to test a scheduled fabric over several months. Given the strong results, ByteDance deployed DriveNets Scheduled Ethernet Fabric in its production AI training environment in July 2024 with great success.
Summary
For ByteDance, carrying out efficient AI training requires more than just deploying thousands of GPUs. It demands a network that can handle synchronized, high-volume traffic with predictable performance, while using standard Ethernet.
By deploying a scheduled Ethernet fabric powered by DriveNets Network Cloud, ByteDance demonstrated that the open architecture not only meets the requirements of large-scale AI training workload, but also surpasses traditional approaches, thereby serving as a viable alternative to InfiniBand.
The solution delivered higher-than-expected performance and simplified operations, creating a scalable, open foundation for ByteDance’s future AI initiatives.
Talk with our AI Experts
Additional AI Infrastructure Resources
- Scaling AI Workloads Over Multiple Sites through Lossless Connectivity
- Resolving the AI Back-End Network Bottleneck with Network Cloud-AI
- Meeting the Challenges of the AI-Enabled Datacenter: Reduce Job Completion Time in AI Clusters
- How is DriveNets revolutionizing network infrastructure for AI and service providers?
- Why InfiniBand Falls Short of Ethernet for AI Networking
- Fastest AI Cluster Deployment Now a New Industry Requirement
- CloudNets-AI – Performance at Scale