The first use of this capability is running multiple routing instances – such as core routing, aggregation and peering – over a shared network infrastructure.
Adding Non-Routing Functions
Another step in optimizing enterprise network infrastructure is adding non-routing functions to the mix, such as security, analytics or mobile (e.g., 5G network) functions.
Deploying functions and services on top of the Network Cloud shared infrastructure enables:
- A welcome shift from hardware centric to software centric network evolution path
- Faster deployment of new services in the network – no need for long and complicated network integration
- Higher utilization of hardware infrastructure
- Improved network performance, with enhanced quality of experience (QoE) for the services running on top of the network
- Simplified network planning and management
Moreover, such network functions, which are smoothly integrated with the DriveNets Network Cloud infrastructure, can be third-party applications selected by operators in a best-of-breed approach.
Let’s review an example of such network functions implemented over a shared Network Cloud infrastructure.
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Protection
DDoS protection is a main security pillar in any public network. The typical approach for such a system implementation is based on two main elements:
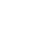
- DDoS controller: The controller receives information (typically via NetFlow) from the network element and runs an analysis to identify DDoS attacks.
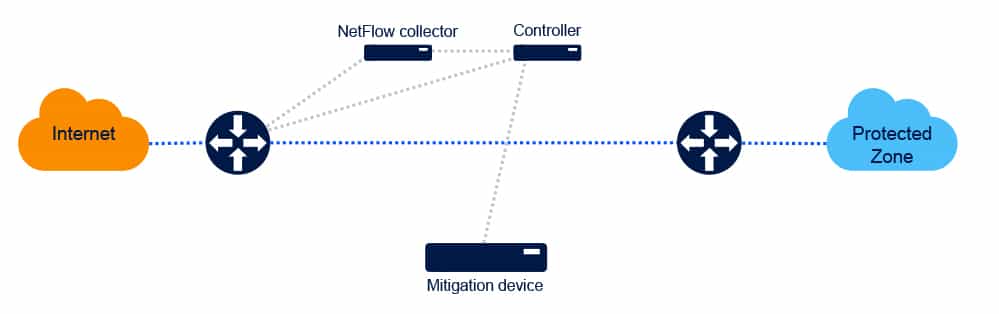
- Scrubbing center: Traffic that is identified as “infected” with DDoS is redirected by the ingress router to a mitigation device; the DDoS elements are then “scrubbed off” and the traffic is routed back to the ingress router.
The following diagrams illustrate this architecture and the traffic flow in first normal and then DDoS modes:
There are two main drawbacks in this type of implementation:
- Scaling: The amount of DDoS traffic that can be mitigated is limited by the physical connectivity between the ingress router and the scrubbing center. In case of a higher-scale DDoS attack, service level degradation and even denial of service are possible.
- Latency: In a DDoS event, a significant amount of non-infected traffic travels from the ingress router to the scrubbing center and back; this adds latency that, in and of itself, degrades the service level.
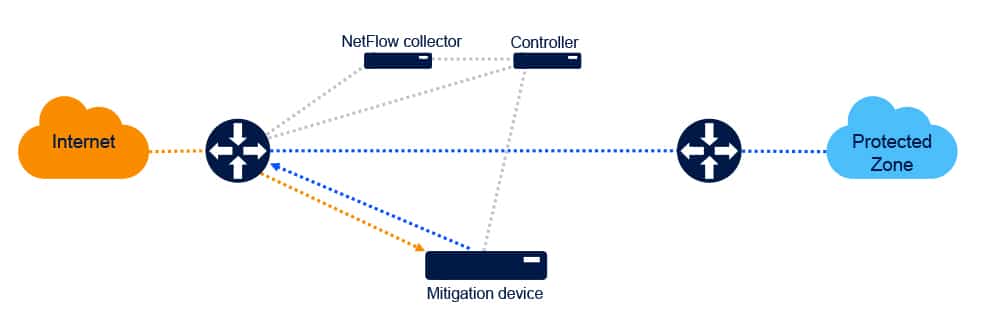
An alternative implementation of the DDoS protection solution leverages DriveNets Network Cloud’s multiservice capability, which, in effect, turns the network itself into the DDoS protection function. This is done by loading the software of the scrubbing center functionality to the Network Cloud infrastructure, as illustrated in the following diagram:
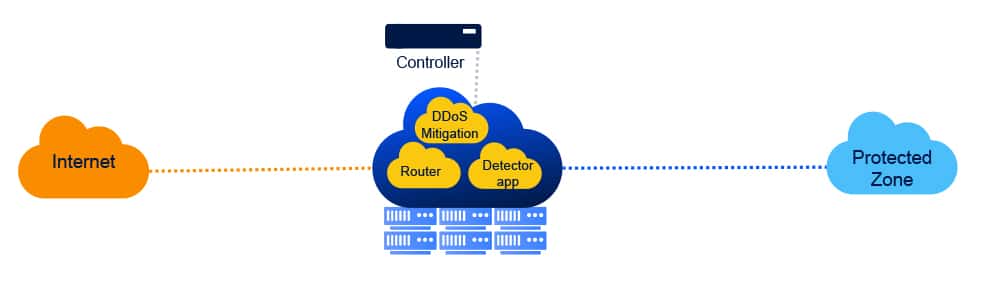
Compared to the typical implementation described earlier, this type of implementation delivers three major benefits:
- Cost reduction: This solution eliminates the need for a stand-alone appliance for the scrubbing center functionality. Instead, the hardware used is part of the shared resource pool that already exists in the site.
- Wire-speed scaling: As the mitigation functionality resides on the same infrastructure as the routing functions, there is no physical limitation on the traffic between the two. The mitigation process is, therefore, not limited in terms of capacity.
- Improved QoE: The scrubbing process is done without traffic redirection; therefore, no additional latency is imposed on the non-infected traffic in the network.
Download White Paper
Multiservice - Maximizing Infrastructure Utilization