|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
InfiniBand vs. Ethernet: A brief overview
To align with the ever-growing demands of data centers, selecting a networking technology for large-scale data centers is more crucial than ever. When it comes to data transmission, InfiniBand and Ethernet compete for supremacy. InfiniBand and Ethernet represent divergent network communication technologies, marked by differences in transmission rates, latency, reliability, scalability, costs and maintenance.
What is InfiniBand?
InfiniBand is a high-speed networking technology primarily designed for high-performance computing (HPC) environments. It offers extremely low latency and high bandwidth, making it suitable for applications that demand predictable and lossless fabric.
Though InfiniBand is a powerful network technology, it is a practically proprietary protocol that comes with significant trade-offs. Its limitations include: long fine-tuning efforts to optimize performance, limited multi-tenancy capabilities, separate networks for compute and storage, and of course a hefty price tag and vendor lock-in. As a result, the industry is looking for alternative solutions that are more cost-effective and free of vendor lock-in.
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet, on the other hand, is a widely adopted networking technology that has evolved over the years to meet the growing demands of data centers. It is the de facto networking standard, with over 600M ports shipped annually. It offers flexibility, scalability and ease of use, making it a popular choice for various applications, including AI networking. So, it seems that the obvious alternative to InfiniBand is Ethernet.
Yet traditional Ethernet is, by nature, a lossy technology that results in higher latency and packet loss, and it cannot provide adequate performance for large clusters. The OCP Ethernet for Scale-Up Networking (ESUN) and the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) Specification 1.0 aims to resolve Ethernet’s drawbacks by adding congestion control and quality-of-service mechanisms to the Ethernet standards, allowing hyperscalers and enterprises to use Ethernet with less performance compromise.
AI networking: comparing InfiniBand and Ethernet
The performance of an AI fabric is best measured by how it is reflected in the application layer. We will now compare InfiniBand and Ethernet performance based on the following parameters:
- Nvidia Collective Communication Library (NCCL) tests
- Bandwidth and latency
- Scalability and flexibility
- Security and management
- Cost-effectiveness and industry adoption
Nvidia Collective Communication Library (NCCL) tests
NCCL is Nvidia’s protocol for data exchange between GPUs. Highly optimized for Nvidia GPUs, NCCL takes advantage of the underlying hardware capabilities, such as Nvidia NVLink and InfiniBand, to achieve high-bandwidth and low-latency communications.
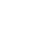
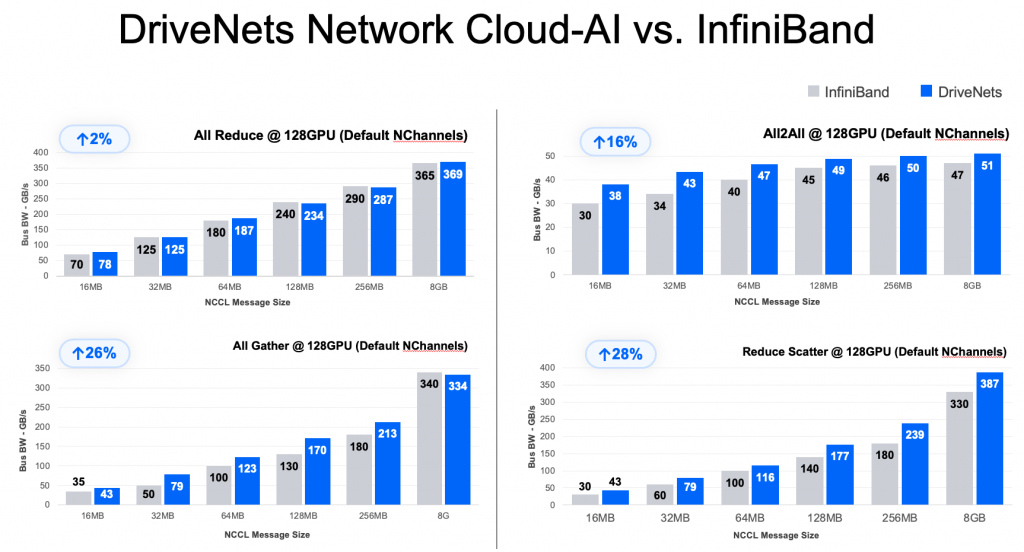
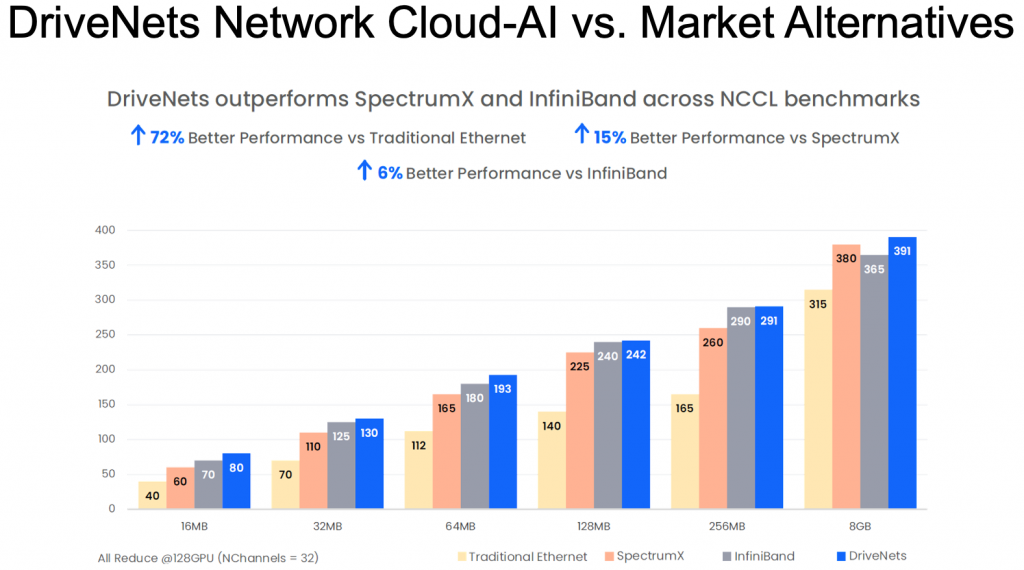
Recently, a live test was conducted on a WhiteFiber deployment in the neocloud’s new GPU cluster at its site in Iceland. The test results clearly demonstrate DriveNets’ consistent performance advantage over all other technologies, including Nvidia’s InfiniBand and Spectrum-X. DriveNets Network Cloud-AI delivers the highest performance Ethernet-based AI back-end fabric, with performance similar to InfiniBand’s.
The test results of DriveNets’ Ethernet solution were compared to three other leading AI networking technologies in the market:
- Nvidia InfiniBand (Quantum-X): The leading technology, InfiniBand is considered the industry benchmark with respect to performance. The DriveNets solution achieved 6% better performance vs. InfiniBand, on average.
*** Competitor results taken from SemiAnalysis testing
- Nvidia Ethernet (Spectrum-X): Spectrum-X is Nvidia’s technology based on Ethernet. The DriveNets solution achieved 15% better performance vs. Spectrum-X, on average.
- Standard or Legacy Ethernet: Used in data center compute clusters, traditional Ethernet is the “default” architecture for non-AI data centers. DriveNets Network Cloud-AI achieved 72% better performance vs. traditional Ethernet, on average.
*** Competitor results taken from SemiAnalysis testing
For more information about the NCCL comparison, see insights from deploying an Ethernet-based GPU cluster fabric webinar.
Bandwidth and latency
InfiniBand excels in terms of raw bandwidth, with its latest XDR (eXtreme Data Rate) generations offering speeds up to 800 Gbps. This high throughput is beneficial for AI workloads that involve massive data transfers. However, Ethernet has also made significant strides, and modern Ethernet technologies such as Tomahawk 6 offer 1.6TbE interfaces. While InfiniBand traditionally offered lower latency, advancements in Ethernet technologies have significantly narrowed the gap, making it a viable option for low-latency AI workloads.
See a short video about Ethernet’s tail latency in AI networks.
Scalability and flexibility
Ethernet’s widespread adoption and compatibility make it highly scalable and flexible. It is compatible with existing data center infrastructure and supports a broad range of devices, making it easier to integrate into diverse network environments. In contrast, InfiniBand may require specific hardware and software configurations, limiting its scalability and interoperability. Ethernet’s compatibility and cost advantages over time give it an edge in traditional infrastructure clusters.
Security and management
InfiniBand lacks Ethernet’s breadth of security and management features, which have been built by Ethernet vendors over multiple decades. Ethernet’s long-standing presence in enterprise and service networks has enabled the development of robust security protocols and comprehensive management capabilities. This makes Ethernet a more favorable choice for organizations that prioritize security and efficient network management in their AI deployments.
Cost-effectiveness and industry adoption
Ethernet’s popularity and mass production have made it more cost-effective compared to InfiniBand. Furthermore, 650 Group research suggests that Ethernet remains the protocol of choice for the vast majority of AI workloads, estimating that 91% of AI workloads will run on Ethernet in 2029. While InfiniBand may have some niche use cases in HPC-like workloads, Ethernet is well-positioned for both external connectivity (front-end networks) and internal compute networks (back-end networks) for varied applications and AI workload types that are connected online.
Nvidia’s plans for InfiniBand
At Nvidia’s GTC 2025 keynote, CEO Jensen Huang emphasized a strategic shift towards alternative Ethernet-based networking solutions for AI infrastructure. This transition is exemplified by Nvidia’s introduction of the Spectrum-X Ethernet platform, which delivers InfiniBand-like capabilities and is designed to connect hundreds of thousands of GPUs in large-scale AI deployments.
While Huang did not explicitly state that Nvidia is abandoning InfiniBand, the company’s roadmap indicates a growing emphasis on Ethernet solutions. Nvidia continues to develop both InfiniBand and Ethernet technologies, as seen in their Quantum-X Photonics (InfiniBand) and Spectrum-X Photonics (Ethernet) switches. However, the focus on Ethernet suggests a strategic pivot toward Ethernet for accommodating the scalability and efficiency demands of modern AI workloads, a trend further reinforced by the adoption of Spectrum-X Ethernet switches by Meta and Oracle, which are leveraging the technology to accelerate their large-scale AI networks…
Effectively leveraging ethernet for AI networking with scheduled fabric
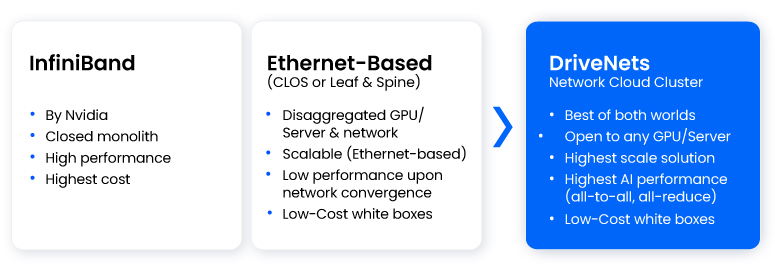
InfiniBand and Ethernet are both powerful networking technologies with unique strengths in different contexts. While InfiniBand traditionally excelled in high-performance computing environments, Ethernet has evolved to meet the demands of modern data centers and AI applications. The DriveNets Network Cloud-AI solution demonstrates how Ethernet can be leveraged effectively for AI networking with Fabric Scheduled Ethernet. DriveNets Network Cloud-AI presents a unique and innovative architecture that offers the high performance and scale of a fabric interconnect solution in production, with the cost-effectiveness of an open, disaggregated cloud solution.
Key Takeaways
- InfiniBand’s Limitations in Scalability and Cost: While InfiniBand has traditionally been favored for high-performance computing due to its low latency and high throughput, it presents challenges in AI networking. These include high costs, vendor lock-in (primarily with NVIDIA), and complexity in scaling across large, distributed AI clusters. Such limitations make it less suitable for the evolving demands of AI workloads.
- Ethernet’s Evolution to Meet AI Demands: Ethernet has matured to address the needs of AI networking. Advancements like DriveNets’ scheduled fabric technology enable Ethernet to provide predictable, lossless, and low-latency performance, matching or surpassing InfiniBand in certain scenarios. This evolution makes Ethernet a viable and cost-effective alternative for AI infrastructures.
- DriveNets Network Cloud-AI’s Performance Advantages: The DriveNets Network Cloud-AI solution demonstrates significant performance improvements. By utilizing a scheduled fabric architecture, it achieves up to 30% better job completion times (JCT) compared to other Ethernet solutions, enhancing resource utilization and efficiency in AI workloads.
- Open and Vendor-Agnostic Architecture: Unlike InfiniBand, which often ties users to specific vendors, Ethernet-based solutions like DriveNets’ offer an open architecture. This openness ensures interoperability, allowing organizations to integrate various hardware components without being confined to a single vendor ecosystem.
- Simplified Operations and Reduced Complexity: Ethernet’s widespread adoption and familiarity among IT professionals simplify deployment and management. DriveNets’ solution further reduces complexity by collapsing traditional network layers into a flat, single-switch architecture, streamlining operations and minimizing the need for extensive fine-tuning.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is Ethernet often considered a cost-effective solution for ai workload networking compared to InfiniBand?
While InfiniBand has traditionally been favored for high-performance computing due to its low latency and high throughput, it presents challenges in AI networking. These include high costs, vendor lock-in (primarily with NVIDIA), and complexity in scaling across large, distributed AI clusters. Ethernet, on the other hand, has matured to address the needs of AI networking. Advancements like DriveNets’ scheduled fabric technology enable Ethernet to provide predictable, lossless, and low-latency performance, matching or surpassing InfiniBand in certain scenarios. This evolution makes Ethernet a viable and cost-effective alternative for AI infrastructures. - How does DriveNets’ Network Cloud-AI enhance Ethernet’s capabilities for AI workloads?
DriveNets’ Network Cloud-AI utilizes a scheduled fabric architecture to transform standard Ethernet into a high-performance, lossless network suitable for AI applications. This architecture collapses traditional network layers into a flat, single-switch design, reducing complexity and latency. It supports up to 32,000 GPUs with 800Gbps connections in a single cluster, achieving up to 30% better job completion times (JCT) compared to other Ethernet solutions. Additionally, its open and vendor-agnostic design ensures interoperability, allowing organizations to integrate various hardware components without being confined to a single vendor ecosystem. - What are the scalability advantages of Ethernet over InfiniBand for AI data centers?
Ethernet offers greater scalability for large AI clusters compared to InfiniBand. InfiniBand requires specialized configurations and often results in network bottlenecks or complexity at scale. In contrast, Ethernet—especially when implemented with DriveNets’ scheduled fabric—supports flat, large-scale architectures with thousands of GPUs, making it easier and more cost-effective to expand AI infrastructure without sacrificing performance or simplicity.
Related content for AI networking architecture
DriveNets AI Networking Solution
Latest Resources on AI Networking: Videos, White Papers, etc
Recent AI Networking blog posts from DriveNets AI networking infrastructure experts
Download White Paper
Utilizing Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) for Back-End AI Networking Fabric