GPU and AI ASIC Diversity Ramps in 2H24
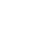
Most of the AI deployments have been done by Nvidia and Google’s TPU (Broadcom). That will change as we look towards the next 12-18 months. AMD (MI300X) and Intel (Gaudi 3) should ramp significantly across many customers soon. At the same time, we expect the custom solutions (mainly Marvell and Broadcom) to ramp up at Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft. Let’s not forget Apple, which is highly ambitious in its AI efforts, as shown during the WWDC in early June. There are also many startups, such as Groq and Cerabras, that are entering with compelling solutions.
DC Semiconductors: Likely 2024 GPU/ASIC Split
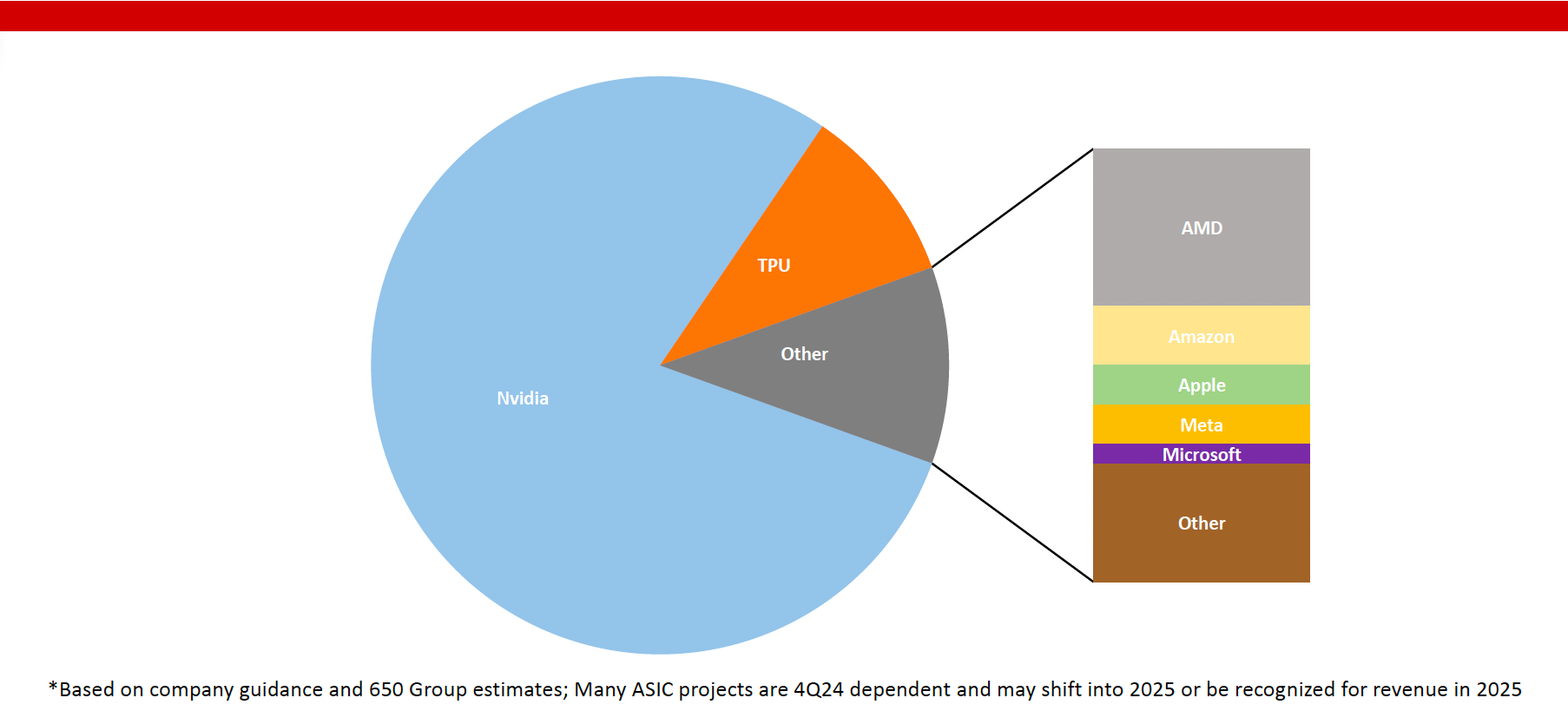
Ethernet, the Fabric of Scale
When a customer only builds a one-off AI system, running on different network topologies is not a big deal. Market data supports this, with most AI back-end networks being InfiniBand. However, as customers use multiple AI ASICs and GPUs, a more standard and robust network fabric becomes critical to enabling GPU and AI ASIC diversity.
Ethernet, with over 400M ports installed inside the data center is ubiquitous, allowing customers to scale AI beyond the one-off systems we have seen and not be stuck with different networking technologies for each AI chip.
Ethernet which is based on an established standard and supports a variety of GPUs and NICs is available from a choice of vendors, offering the best option for companies seeking AI diversity and would like to avoid being locked to a single-vendor solution. Standardizing on Ethernet allows AI operations teams to be more efficient and deepen their skill sets.
Ethernet Performance Optimized for AI
Ethernet is based on a ’best-effort’ delivery over a simple hardware design, forcing the end-points to ensure transmission reliability. In the AI world where performance and scale are very high and compute is costly, both the network and the NIC at the endpoints need to maximize the performance, reduce packet loss, and accelerate failure recovery. This will optimize the performance of the entire AI cluster and reduce the waste of costly AI-compute resources.
This is the mission of the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) which is supported by most hyperscalers and leading networking vendors – to deliver a complete architecture that optimizes Ethernet for high-performance AI. The work of UEC will also drive the adoption growth of Ethernet in AI.
Ethernet Switch Data Center: Total Market Revenue
Ethernet Accelerates Innovation
The Ethernet roadmaps for AI is robust with rapid generational changes going forward. 2024 will be the year of significant 800 Gbps deployments, and 1.6 Tbps will be right around the corner. Back-to-back chip release schedules will push Ethernet from 12.8 Tbps to 102.4 Tbps per chip in under two years. AI ASIC and GPU suppliers can use the increased cadence of network introductions to come out with products more quickly or enhance offerings, ensuring that their GPUs are fed more than enough data from the network for training and inference.
DriveNets Provides Open AI Solutions
DriveNets high-performance Ethernet is already deployed at a Hyperscaler, showing vital AI/ML performance metrics across multiple silicon families. Its lossless fabric supports high-performance AI networking with any NIC, allowing lower power consumption and adoption of any new AI hardware. It also supports a choice of networking white boxes from multiple vendors, therefore reducing infrastructure OpEx and CapEx compared to single-vendor solutions. In addition, DriveNets’ solution does not need fine-tuning per AI workload type, further simplifying network operations. Ultimately, AI vendors will want to move to fewer tiers and consistent networks across their entire AI/ML infrastructure.
Related content for AI networking architecture
DriveNets AI Networking Solution
Latest Resources on AI Networking: Videos, White Papers, etc
Recent AI Networking blog posts from DriveNets AI networking infrastructure experts
Download white paper
Utilizing Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) for Back-End AI Networking Fabric