What is Network Disaggregation?
The rise of network disaggregation in the telecom industry takes a page from the cloud-native revolution that took place with compute and storage for hyperscalers.
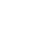
Essentially, network disaggregation is the separation of hardware and software components that carry out the main functions of a network on switches, routers, and other traditional and monolithic networking hardware. Disaggregating the network infrastructure allows service providers to enhance their deployment and management processes while reducing costs and improving security.
After implementing network disaggregation, service providers can manage the hardware and software components of their networking infrastructure at scale independently.
This is done using:
- a centralized management system, such as a network management platform or software-defined networking (SDN) controller, helping service providers manage and oversee all their networking infrastructure’s hardware and software components
- automation tools, enabling service providers to easily provision and configure new hardware and software components
- open networking standards, like Open Network Install Environment(ONIE), allowing service providers to integrate hardware and software components from different vendors
Functional Components of Network Disaggregation
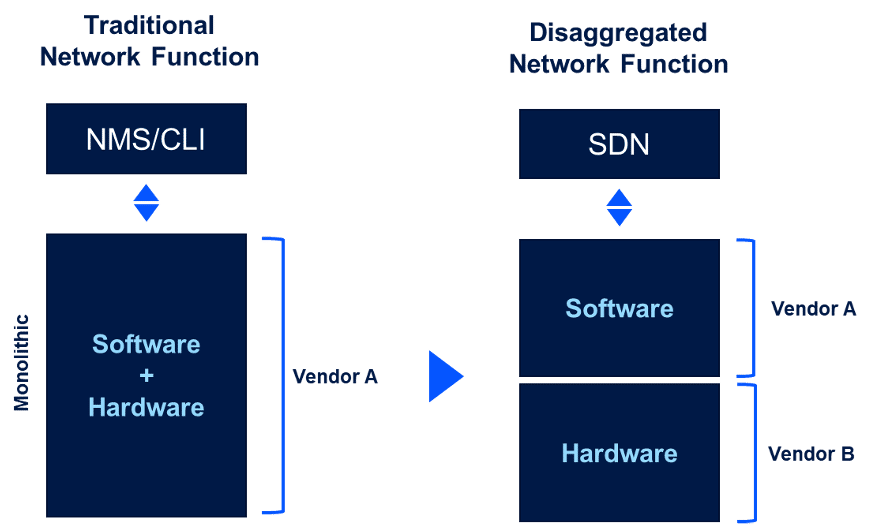
Network disaggregation is about the abstractions that decouple software and hardware components, making them much simpler to swap and replace. Hardware abstractions mask the details for the Network Operating System (NOS) platform to integrate with networking silicon (white box networking), that can be sourced from multiple vendors. Network disaggregation is software-based, making them much leaner and more scalable than their monolithic predecessors. For instance, to increase the capacity of a disaggregated network, operators can simply add low-cost white boxes to their networks and turn on new software licenses rather than add a whole new chassis-based system.
More Levels of Network Disaggregation
Additional levels of network disaggregation usually derive from breaking a network function into multiple components. An example is breaking the cellular base station into a central unit (CU), distributed unit (DU) and radio unit (RU). In the IP networking world, such multi-level disaggregation includes the separation of the control plane and the user plane, and the separation of the packet-forwarding functionality and the fabric functionality.
Network Disaggregation Operations
Disaggregated networks can have a smaller physical footprint than their traditional alternatives, with infrastructure that is significantly less energy-intensive to produce. Hardware and software can be deployed in minutes using zero-touch provisioning. Plus, the capacity of any dimension of a system can be upgraded without throwing away existing infrastructure, offering telcos the agility, simplicity, and scalability they need.
Breaking Vendor Lock with Network Disaggregation
Disaggregation offers a better way to build networks, allowing network operators to regain control of their networks from incumbent vendors who have dominated the industry for decades.
Though many operators may rationalize their single- (or dual-) vendor environments through familiarity and availability of support, this comfort comes at a price. With higher list prices than disaggregated alternatives, proprietary platforms also limit agility and have hindered innovation, often requiring costly upgrades, while constraining access to new technologies.
With supply chain disruptions becoming a fact of life today, network disaggregation equips telcos to better manage supply chain shocks. Rather than relying on a single vendor for both hardware and software – and being forced to delay development when the vendor’s specific network hardware isn’t available – network disaggregation frees telcos to buy any white-box hardware that is available on the market.
Pros & Cons of Network Disaggregation?
Network disaggregation allows organizations to mix and match hardware and software components from different vendors. This enables them to choose the best solutions for their specific needs and take advantage of the latest technologies from multiple vendors. For example, service providers can choose to use white-box hardware from different vendors and open-source software on top of standard hardware. In addition, network disaggregation enables service providers to update and upgrade individual network components without relying on a single vendor for updates. This can reduce costs and improve security, as service providers can choose components that not only meet their current security requirements but also can be easily updated to address new security threats.
There are, however, limitations to network disaggregation. Compared to traditional, monolithic networking systems, disaggregated networks are more difficult to implement and manage as they require additional skill sets from service providers. They also require a management system that can make implementing and maintaining the network more expensive. Lastly, troubleshooting disaggregated networks can be more challenging because more components and layers are involved. These limitations can be overcome by working with a disaggregated networking vendor that takes responsibility for these issues.
Network Disaggregation is a Step Forward
Network disaggregation has broken down the traditional, monolithic architecture of network functions into smaller, modular components that can be independently managed by service providers while retaining the same overall network functionality.
While this evolution is not complete, it has enabled the industry to take a larger step forward toward network virtualization and cloud networking.
DriveNets Disaggregated Network Solution
The DriveNets Network Cloud is a distributed disaggregated network solution, that applies the success hyperscalers achieved in computing infrastructure to high-scale networks. Network Cloud offers service providers (SPs) similar optimal efficiency, enabling them to streamline their most complex operations.
Additional Resources for Network Disaggregation
Blog
- Making Network Disaggregation a Reality
- Disaggregated Routing and the Multiservice Network Cloud
- Analysys Mason: Network Disaggregation is a Reality for CSPs IP Networks
- Realize the Operational Benefits of Network Disaggregation
- Disaggregation is Transforming High-Scale Networks, Now
Video
- Why Operators are Embracing Network Disaggregation
- Telecom Transformation – Disaggregation, Software, Cloud
- Season 3 Ep 1: Disaggregation Mythbusters
- Season 3 Ep 4: Service Provider Panel at MWC
- DriveNets Discusses Network Disaggregation with Packet Pushers
White Paper