What is the Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC)?
Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) is an innovative networking architecture for building large-scale routing systems. DDC delivers similar functionality as traditional monolithic routers but with better scalability and flexibility. DDC introduces two key innovations: the disaggregation of software and hardware components and the ability of a network operating system (NOS) to unify dozens of distributed white boxes to operate as a single network entity.
Why do service providers need a Distributed Disaggregated Chassis?
Service providers recognize the changing landscape of the networking industry. Traditional hardware-centric solutions are unable to meet the rapidly increasing volume of IP endpoint traffic from the access network. In addition, over-the-top (OTT) services and hyperscaler dominance have impacted revenue. In response, service providers are actively searching for a new flexible, scalable and cost-effective networking solution.
What are the key features of the Distributed Disaggregated Chassis?
Disaggregation
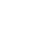
DDC breaks up the traditional monolithic chassis into separate hardware (HW) and software (SW) building blocks, while carrying out the main functions of traditional monolithic networking hardware. Disaggregation enables service providers to manage hardware and software independently, and thereby mix and match HW and SW from multiple vendors to increase cost savings. In addition, the disaggregated approach enables SPs to enhance resilience by supporting component upgrades or replacements without impacting the entire network.
Unified System Design
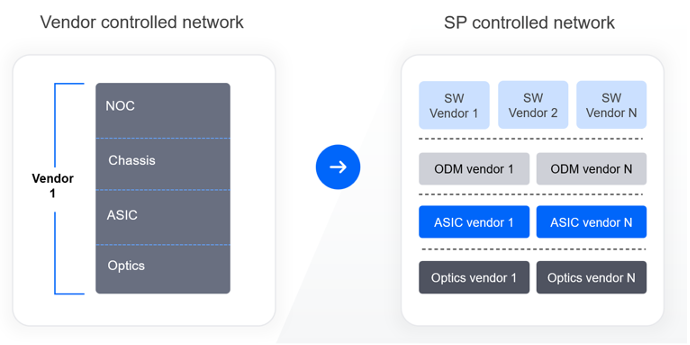
With DDC, traditional chassis hardware is broken down into separate, standardized building blocks. Each component, such as line cards, fabric cards or controllers, is transformed into white boxes not bound by any chassis limitation. This network design enables service providers to build routers of any size across all network domains by using the same cost-effective white boxes. Additionally, this unified approach significantly reduces planning, procurement, and operational efforts.
Network Operating System (NOS) and a Single Network Entity
In a DDC cluster, multiple distributed white boxes are used to build a large-scale network. This architecture combines the best of both centralized and distributed characteristics. On the one hand, individual components enhance resilience and minimize the impact of failures (aka blast radius). On the other, the cluster’s NOS orchestrates the entire cluster, regardless of size, as a single network entity that is easy to manage and operate.
What are the benefits of the Distributed Disaggregated Chassis?
Distributed Disaggregated Chassis offers not only a more flexible and modern network design but also greatly enhances the operational experience for service providers.
Break the Vendor Lock
- Lower cost – disaggregated ASIC, ODM, NOS, optics, and services
One of the fundamental benefits of DDC is the elimination of vendor lock-in. SPs can mix and match any suitable components from a wide range of available ASICs, hardware, software and optics vendors. This versatility ensures that service providers are not restricted to specific brands or technologies, fostering a competitive and innovative ecosystem tailored to their needs.
- Proven in the world’s largest networks
DDC is not just a theoretical advancement; it has been tested and proven in multiple real-world scenarios. This field-proven technology demonstrates its reliability and effectiveness in managing the diverse and dynamic requirements of modern networks, ensuring that service providers can confidently transition to DDC with minimal risk.
- Sustainability and circular economy – one whitebox for any use case
DDC contributes to reduced environmental impact and promotes a more sustainable approach to network management by optimizing resource utilization and extending the lifespan of existing infrastructure. DDC advocates for a unified hardware approach across the entire network, from core to metro-edge and aggregation, enabling the same standard white boxes to be used across all network domains.
Simplified operations
- Unified HW – core to metro edge / aggregation – efficient warehousing
DDC HW unification simplifies the network architecture, streamlines management, and reduces the complexity associated with operating diverse systems. Network components are reduced from tens of HW/SW elements to two white boxes and a single software package. With fewer unique parts to store and manage, service providers can benefit from reduced inventory costs and a more efficient supply chain.While DDC clusters contain numerous distributed white boxes, their control plane is centralized and managed as a single network entity. - Higher availability– simplified hardware, smaller blast radius, ISSU
By its design, DDC enhances network availability. Its distributed nature and redundancy mechanisms ensure continuous operation, minimizing downtime and ensuring reliable service delivery. Maintenance is easily accomplished by replacing individual white boxes, thereby eliminating the need for cumbersome forklift chassis replacements and disruptive maintenance windows.
- Leaner design – collapsing network layers
A key advantage of DDC architecture is its ability to streamline network infrastructure by collapsing multiple networking layers into a more simplified structure. This collapsing of layers not only drives down complexity but also reduces latency, improves performance, and lowers operational costs.
Software-based Innovation
- Accelerated feature delivery
DDC represents a paradigm shift in network architecture, driven by software-based innovation. By leveraging cloud-native principles, DDC offers a level of flexibility and agility previously unattainable in traditional network setups. This approach allows for rapid deployment of new services and easier integration with third-party applications. - Elastic scale
By stacking low-cost white boxes for incremental capacity upgrades, like in cloud environments, SPs can elastically scale out the DDC cluster whenever needed, one white box at a time. This approach avoids unnecessary up-front investments, supports efficient capital expenditure (CapEx) management, and ensures that the network grows with demand.
Distributed Disaggregated Chassis gains momentum with service providers
Leading service providers such as AT&T and KDDI have already made significant deployments of DDC solutions across their live networks using DriveNets Network Cloud. Their efforts align with other network operators like Comcast, Vodafone, MTN, Telefonica and Orange, which also are adopting open and disaggregated networks. SPs that already have implemented disaggregated solutions have achieved cost reductions, accelerated innovation, and improved scalability.
The Future of Disaggregated Solutions
In October 2023, in collaboration with AT&T, UfiSpace, HPE and Intel, DriveNets’ contribution to the Open Compute Project (OCP) DDC specification version 3 was accepted. Based on DriveNets Network Cloud architecture, this latest version specifically addresses mobile backhaul infrastructure, as well as Ethernet networking for high-performance AI workloads in large-scale clusters.
Real-world applications of DDC can be seen through case studies of major telecom companies. Detailed analyses of the operational and economic impacts of DDC are illustrated by case studies of Comcast (SCTE) and KDDI. These insights show a clear picture of how DDC is reshaping the landscape of network infrastructure, offering a path towards more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective network management.
DriveNets Distributed Disaggregated Chassis meets industry standards
DriveNets was one of the first vendors to be awarded a Telecom Infra Project (TIP) Requirements Compliant Ribbon for a Distributed Disaggregated Backbone Router solution, following the initial phase of TIP’s test & validation process which evaluated industry readiness and solutions availability for disaggregated core networking.
Additional Resources for Distributed Disaggregated Chassis
-
Video
- Distributed Disaggregated Chassis
- The Operational Impacts of Supporting a Disaggregated, Distributed, Cloud-based Network Architecture
- MWC Telecom Transformation – Disaggregation, Software, Cloud
- OCP Global Summit 2022: Distributed Disaggregated Chassis Routing System Evolution
- Why Operators are Embracing Network Disaggregation
- Disaggregation Mythbusters (CloudNets S3 Ep 1)
- Distributed Disaggregated Networks (CloudNets S1 Ep 2)
- Disaggregated Networks Standardization (CloudNets S1 Ep 10)
-
White Paper
-
Blog
- Which Network Architecture is Right For You: A Comparison of Chassis-based, Clos, and Distributed Disaggregated Chassis
- One Network Doesn’t Fit All
- Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) V2 Makes Network Operations Even Simpler
- Our Hands-on Experience in Building Better Networks
- Top 5 Benefits of a DDC Architecture for MSO Networks