What is network infrastructure?
Network infrastructure refers to the primary components that enable communication and data transfer between devices and systems within a network. In simpler terms, it is what makes the internet and other networks possible.
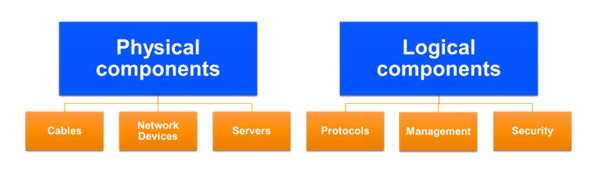
Network infrastructure consists of physical components such as cables, routers, switches and servers, which facilitate data transport. Additionally, logical components such as software applications, protocols and security measures are used to manage and secure network traffic.
What are the main building blocks of network infrastructure?
Generally, network infrastructure is composed of two main types of building blocks : physical and logical.
Physical components of network infrastructure include:
- Cables: In a network, cables are used to connect devices. They come in different types, such as Ethernet cables, fiber-optic cables and coaxial cables.
- Network devices: Network devices transport data packets between devices and networks to their intended destinations. They come in various sizes to accommodate different network sizes, and they prevent unauthorized access by using firewalls and other security measures.
- Servers: These are dedicated computers that provide services such as storage, email, web-hosting, databases and other applications.
Logical components of network infrastructure include:
- Protocols: A network protocol describes how devices communicate and exchange data over a network. Examples include TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP and DNS.
- Management: Management tools and software are used to monitor, troubleshoot and manage network resources and performance.
- Security: This includes the use of policies, network segmentation, virtual private networks (VPNs) and other security measures to protect the network and its data from unauthorized access, attacks and malware.
What is well-designed network infrastructure?
Every organization that relies on technology needs a well-designed network infrastructure. With solid network infrastructure in place, businesses can incorporate new technologies and applications as they emerge, enabling organizations to stay up-to-date and competitive in their respective markets.
Service providers must aspire to build a well-designed network infrastructure that can deliver flexible scalability, high availability and optimized load balancing. These features are crucial for maintaining seamless and reliable connectivity, which is critical for modern businesses and organizations. Additionally, since no network is completely immune to outages, it’s also essential to have simple network design and automated management tools (like network orchestration) that enable network administrators to identify and resolve issues promptly. With these in place, service providers can minimize downtime and ensure that their networks remain accessible and function optimally.
What are the main network infrastructure trends?
Technological advancements, changing business needs and increasing demands for speed, security and scalability drive constant evolution in network infrastructure. Some of the main network infrastructure trends to watch for include:
- 5G networks: Faster speeds, lower latency and greater connectivity are expected to be enabled by 5G networks.
- Network disaggregation: This aims to separate the hardware and software components of networking equipment, such as switches and routers. The goal of network disaggregation is to provide more flexibility, cost savings and innovation in network design and management.
- Network automation: Orchestration automation tools are revolutionizing network infrastructure management. They enable faster deployment, enhanced agility, and improved security of network infrastructure.
- Cloud transformation: A shift towards cloud computing is changing network infrastructure, with more networks adopting cloud-based network infrastructure solutions to increase scalability and reduce costs.
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to the source of the data has become popular due to its ability to address the challenges posed by the growing number of connected devices and the increasing demand for low-latency, secure and cost-effective data processing.
- Network security: Cyberattacks are becoming more frequent and complex, making network security a top priority for organizations. As a result, more advanced security solutions are needed.
Network infrastructure in a nutshell
Network infrastructure is the backbone of any modern organization, enabling communication and data transfer across devices and systems. To build a reliable and scalable network infrastructure, service providers need to adopt a combination of different technologies and approaches. These include network disaggregation, network automation, cloud networking and security orchestration.
By leveraging these trends, organizations can build a network infrastructure that meets the demands of modern business operations, ensuring both reliable and scalable networks.
Network infrastructure challenges
Network operators worldwide face increased traffic driven by multimedia consumption, mobile devices, and the arrival of IoT. According to the Cisco Annual Internet Report, IoT connections will grow from 6.1 billion in 2018 to 14.7 billion in 2023, and machine-to-machine (M2M) applications like connected vehicles are growing at a 30% CAGR. Also, mobile connection speeds will increase threefold, while fixed broadband will grow at almost 2.5 times in the 2018-2023 timeframe. All this simply means that network infrastructure needs ongoing investments to keep up. Analysts predict an acceleration in 5G infrastructure build-out to keep up, along with lighting up of fiber assets in the transport and core networks to ferry the increased traffic.
Service providers (SPs) continue to invest large amounts of capital to scale their networks and meet the growing demand for data traffic, while facing reduced revenue due to losing monetization opportunities to over-the-top (OTT) services and hyperscalers. The traditional hardware-centric approach is incapable of meeting the increasing demands for new services and traffic from the access network.
DriveNets meets network infrastructure challenges
Continuing with legacy hardware-centric solutions is no longer viable, as this approach has resulted in a shift in the value scale that favors hyperscalers and OTT service providers. Meanwhile, SPs find themselves burdened with never-ending network investments required to keep up with ever-evolving market demands. The need for service providers to balance cost vs. scalability prompted infrastructure transformation towards a more balanced and flexible network.
Service providers understand that disaggregation is a necessity that cannot be avoided in order to keep up with the rapidly changing technological landscape and the increasing demands of their customers. Ultimately, it is indisputable that the legacy model is no longer viable, and that a move towards disaggregation is necessary for the continued success of service providers.
The modern distributed disaggregated chassis (DDC) router model defined by the Open Compute Project (OCP), which is complemented by the Telecom Infra Project DDBR, offers an alternative to chassis-based routers. DDC/DDBR supports scaling of network capacity just by adding white boxes to an existing network infrastructure cluster, acting as a single entity (of up to hundreds of elements in a cluster). This is opposed to a traditional router chassis that forces service providers to buy multiple and varied sizes of boxes from the same family to accommodate different scaling options.
Based on the Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) model, DriveNets Network Cloud orchestrates a distributed and disaggregated network function that turns simple “off-the-shelf” white boxes into a shared resource supporting multiple network services in the most efficient way possible. DriveNets Network Cloud is a risk-free, battle-proven solution that is already successfully running on global tier-1 carriers’ networks, delivering high availability, multi-level redundancy and seamless maintenance.
DriveNets Network Cloud enables service providers to build their networks like the cloud, offering a truly flexible and cost-effective network architecture that also can address the key challenges that may arise when adopting a new network infrastructure solution.
Additional Network Infrastructure Resources
Service Provider Routing Solutions
Brochure: DriveNets Network Cloud service provider routing solution
Case Studies
- Migrating an IP/MPLS core network to a disaggregated and distributed cluster architecture
- DIGI: Handling Peak Traffic Workloads and Streamlining Core Network Operations
Press releases
- DriveNets Network Cloud Now Carries More Than 52% of AT&T’s Core Production Traffic
- AT&T deploys DriveNets Network Cloud in their next-gen core
- DriveNets and KGPCo Partner to Lead Market Adoption of Disaggregated Core and Edge Networks at Tier 1 Communication Service Providers
White papers